In the modern era of automotive technology, the Car Driver Assistance System (CDAS) has become a crucial aspect of driving safety and efficiency. This technology not only enhances the driving experience but also plays a pivotal role in reducing road accidents. If you are new to this technology, this guide will walk you through the basics of CDAS and how it interlinks with advanced fleet management software, a necessity for contemporary vehicle management.
Understanding the Car Driver Assistance System
What is Car Driver Assistance System?
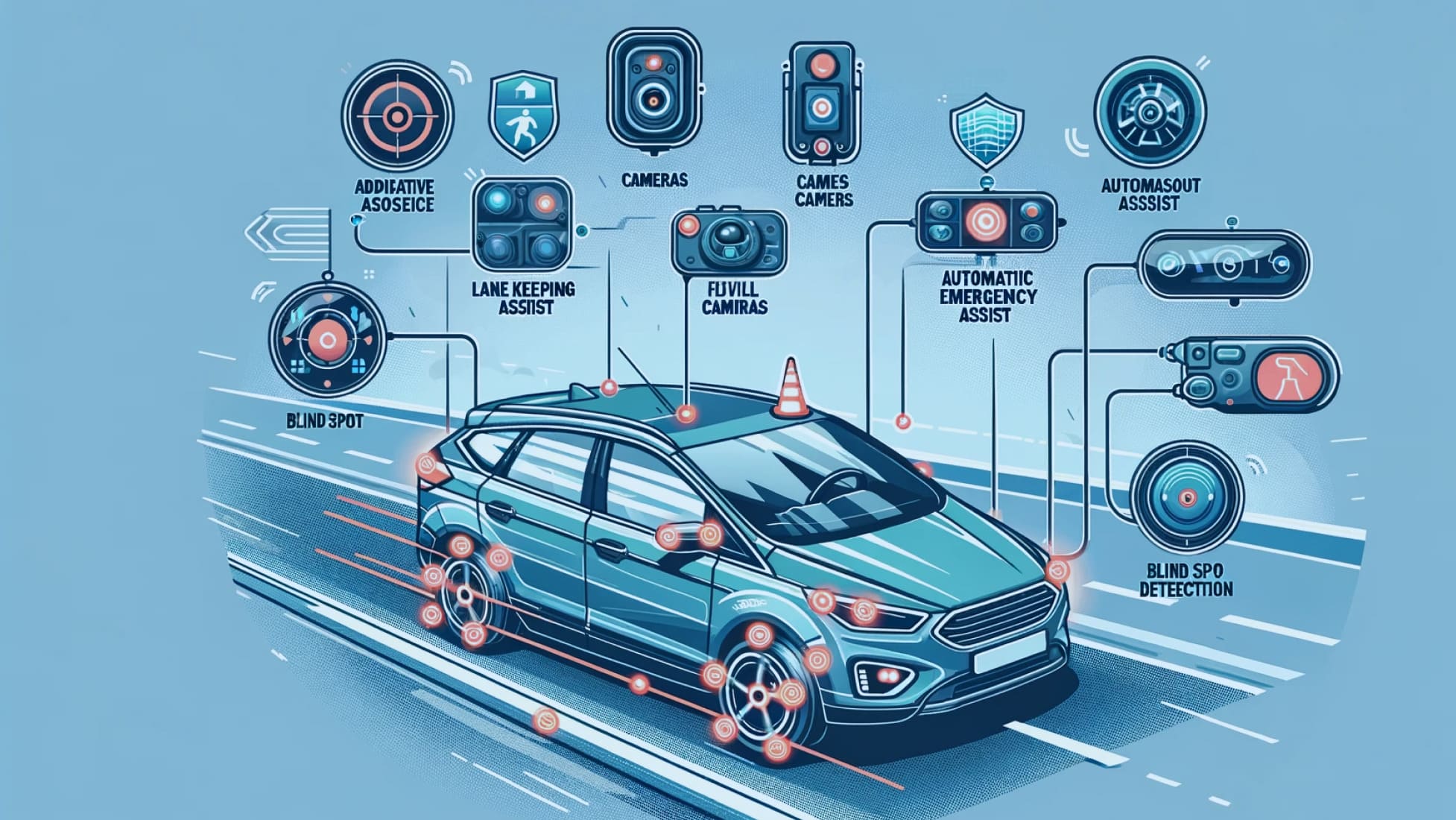
The Car Driver Assistance System refers to a collection of electronic technologies that assist drivers in driving and parking functions. These systems use advanced technologies like sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to help reduce the burden on drivers, enhancing safety on the roads.
The Foundation of CDAS: Sensors and Cameras
At the heart of any Car Driver Assistance System are sensors and cameras. These are the eyes and ears of the system, providing the necessary data to aid in decision-making. Here’s how they work:
- Sensors: These include radar, LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and ultrasonic sensors. They detect objects around the vehicle, measure distances, and even identify traffic signs.
- Cameras: Positioned around the vehicle, these cameras provide visual feedback, helping in lane detection, traffic monitoring, and providing a view of blind spots.
How CDAS Enhances Driving Safety
The primary aim of CDAS is to reduce human error, which is a leading cause of road accidents. Here’s how various CDAS features contribute to safety:
- Collision Avoidance: By constantly monitoring the surroundings, CDAS can warn drivers of potential collisions and even take automatic action to avoid them.
- Lane Departure Warnings: These alerts prevent unintentional lane drifting, a common cause of accidents on highways.
- Adaptive Headlights: They adjust the direction and range of the vehicle’s headlights based on speed, steering, and the elevation of the road, improving night-time visibility.
Key Components of CDAS
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): This function maintains a set speed and distance from the vehicle ahead, automatically adjusting the speed to maintain safety.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): LKA alerts the driver or automatically steers to keep the vehicle within its lane.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): This system detects potential collisions and automatically applies the brakes to avoid or minimize impact.
- Blind Spot Detection (BSD): BSD alerts drivers to vehicles in their blind spots, improving lane change safety.
- Parking Assistance: This includes rear-view cameras and automated parking systems, simplifying the parking process.
The Evolution of CDAS in Modern Vehicles
The evolution of the Car Driver Assistance System (CDAS) in modern vehicles is a testament to the rapid advancements in automotive technology. This journey from basic functions to highly sophisticated systems reflects the industry’s commitment to safety, efficiency, and driver comfort.
Early Stages of CDAS
- Initial Features: The early versions of CDAS were limited to simple functions like parking sensors and basic cruise control.
- Focus on Safety: Initial systems primarily focused on safety features, such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC).
The Rise of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
As technology progressed, CDAS evolved into what is known today as Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS):
- Integration of Sensors and Cameras: The integration of radar, LIDAR, and cameras allowed for more complex functions like adaptive cruise control and lane keeping assist.
- GPS and Navigation Integration: The inclusion of GPS technology improved navigation and route planning, leading to more efficient driving experiences.
The Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AI marked a significant leap in the evolution of CDAS:
- Predictive Analytics: AI allowed systems to analyze vast amounts of data, predicting potential hazards and suggesting preventative measures.
- Learning from Experience: Machine learning algorithms enabled these systems to improve over time, adapting to different driving styles and environments.
Connectivity and Communication
The latest stage in the evolution of CDAS is its connectivity with other systems and infrastructure:
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: This technology allows vehicles to communicate with each other and with road infrastructure, enhancing safety and traffic management.
- Integration with Smart City Infrastructure: CDAS can now interact with smart city systems, like traffic signals and road sensors, to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
With the advancement of CDAS, new challenges and ethical considerations have arisen:
- Cybersecurity Concerns: As vehicles become more connected, they are more susceptible to cybersecurity threats, necessitating advanced security measures.
- Ethical Decision Making: With systems capable of making decisions, questions arise about programming ethics and liability in the event of an accident.
The Future of CDAS
Looking ahead, the evolution of CDAS is likely to focus on:
- Autonomous Driving: The ultimate goal is fully autonomous vehicles, where CDAS takes over most, if not all, driving functions.
- Personalization and User Experience: Future systems will likely offer more personalized experiences, adapting to individual preferences and needs.
- Sustainability: As environmental concerns grow, CDAS will play a role in promoting eco-friendly driving practices, contributing to the broader goal of sustainability in transportation.
The Connection Between CDAS and Fleet Management Software
In the realm of fleet management, integrating CDAS with advanced software solutions is a game-changer. Fleet management software enhances the functionality of CDAS by providing real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance alerts, and efficient route planning. This integration leads to improved safety, reduced operational costs, and enhanced fleet efficiency.
Benefits of Integrating CDAS with Fleet Management Software
- Enhanced Safety: Real-time monitoring of vehicle systems and driver behavior leads to a reduction in accidents.
- Predictive Maintenance: Early detection of potential vehicle issues reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
- Efficient Route Planning: Optimal routing based on traffic and road conditions saves time and fuel.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Fleet managers can make informed decisions based on the comprehensive data provided by the software.
Trends in Car Driver Assistance Systems
The trends in CDAS are constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging regularly. These trends include increased automation, integration with smart city infrastructure, and the use of artificial intelligence for predictive analysis. Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to leverage CDAS for safety and efficiency.
The Future of CDAS: Autonomous Driving
The ultimate goal of CDAS technology is to pave the way for fully autonomous vehicles. While we are not there yet, each advancement in CDAS brings us closer to this reality, promising a future where driving is safer, more efficient, and more accessible.
Tips for Using Your Car’s Driver Assistance System
Familiarize Yourself with the System
Take the time to understand the specific CDAS features available in your vehicle. Refer to the owner’s manual or seek guidance from the dealer.
Stay Alert
While CDAS provides significant assistance, it is not a substitute for attentive driving. Always stay alert and keep control of your vehicle.
Regular Maintenance
Ensure that the sensors and cameras of your CDAS are regularly checked and maintained for optimal performance.
Understand the Limitations
CDAS has limitations, such as reduced effectiveness in bad weather. Understand these limitations to avoid over-reliance on the system.
Conclusion
The Car Driver Assistance System represents a significant leap forward in automotive safety and efficiency. Its integration with advanced fleet management software further enhances its capabilities, making it an indispensable tool in modern driving and fleet management. By understanding and effectively using CDAS, drivers and fleet managers can ensure safer roads and more efficient vehicle management.
Remember, as technology evolves, staying informed and adapting to new trends in CDAS will be crucial in leveraging its full potential. Whether you’re a new driver or a seasoned fleet manager, embracing these advancements will pave the way for a safer and more efficient driving future.


